LED packaging is one of the most important components in LED lighting PCBs and is widely used in various fields. To clarify the concepts of LEDs and LED packaging, here is a brief introduction to LEDs and LED packaging.
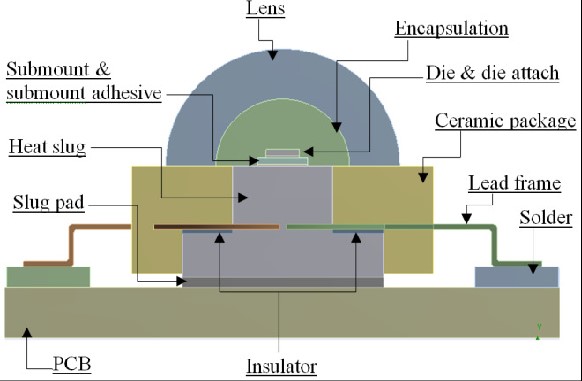
Definition of LEDs:
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode, which is a solid-state semiconductor lighting device and a major component of lighting PCBs.
Part 1 - LED Lighting PCBs
LEDs use solid-state semiconductor chips as the light-emitting material. When a forward voltage is applied, the semiconductor's carriers recombine, producing photons and emitting light. LEDs can emit different colors of light, including red, yellow, blue, green, cyan, orange, purple, and white.
The basic structure of an LED is an electroluminescent semiconductor material placed on a leaded support and encapsulated with epoxy resin to protect the internal circuitry. Therefore, LEDs have good shock resistance.
LED Colors:
LEDs are made from different metal compounds that can emit different colors of light. For example, red LEDs contain aluminum gallium phosphide, while green or blue LEDs contain gallium nitride.
Here are the typical peak wavelengths for several common colors of LEDs:
- Blue - 470nm
- Blue-green - 505nm
- Green - 525nm
- Yellow - 590nm
- Orange - 615nm
- Red - 625nm
- And so on
LED Packaging
The goal of LED packaging technology is to improve light output efficiency, color performance, and device reliability.
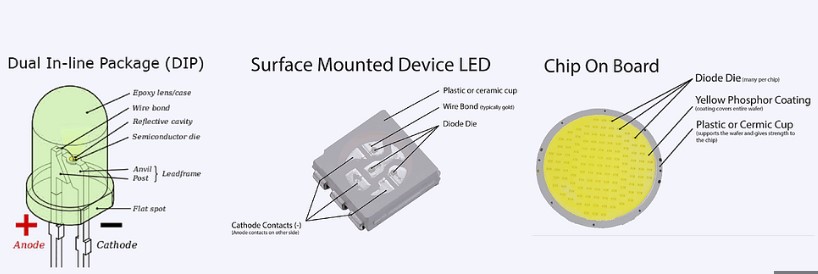
1. Improving Light Output Efficiency
The light output efficiency of LED packaging can typically reach 80% to 90%.
- Use more transparent packaging materials with transparency greater than 95% (1mm thickness) and a refractive index greater than 1.5.
- Adopt fluorescent powders with high excitation efficiency, high color rendering index, and appropriate particle size.
- Design substrates with high reflectivity and high light output using optical shapes.
- Use appropriate packaging techniques, especially coating techniques.
2. Improving Color Performance
The main color performance parameters of LED packaging include luminance, glare, color temperature, color rendering index, color tolerance, and light flicker. Packaging should use multi-primary color combinations to improve the spectral distribution of LED emission and approach the spectral distribution of sunlight.
3. Enhancing Device Reliability
LED reliability includes performance variations under various conditions and various failure mode mechanisms (such as degradation of LED packaging materials and the impact of comprehensive stress). Currently, LED devices can have a lifespan of 50,000 to 100,000 hours.
- Use suitable LED packaging materials with good bonding strength, low stress, good compatibility, good air tightness, temperature resistance, moisture resistance, and UV resistance.
- Implement effective LED heat dissipation using high thermal conductivity, high electrical conductivity substrates, and die attach materials with high thermal conductivity, high electrical conductivity, high strength, and low stress.
- Employ appropriate LED packaging techniques, such as chip mounting, wire bonding, and encapsulation, ensuring strong bonding strength and low stress while demanding bond compatibility.
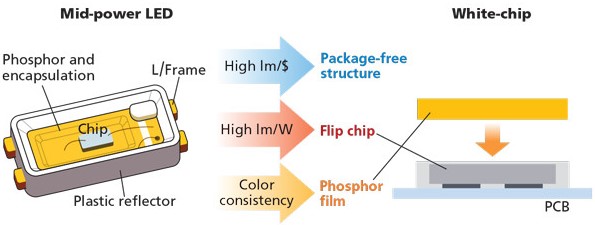
Typical LED Packaging Types
1. Chip-on-Board (COB) LED Packaging
COB LED packaging can be divided into various structures such as MCOB, COMB, MOFB, MLCOB, etc. COB LED packaging technology has become increasingly mature, and its advantage lies in its low cost.
Manufacturers directly bond multiple LED chips (usually nine or more) onto a substrate to form a single LED module. This approach saves space, and compared to standard LED packaging of the same area, COB LED packaging has a larger emitting area and higher light output per square inch.
Similar to miniaturized LED lighting PCBs, COB LED packaging typically uses aluminum and ceramics as substrates for better heat dissipation. However, due to the fact that COB LED packaging can accommodate multiple LED chips with only one circuit, its color performance is relatively limited.
Currently, COB LED packaging accounts for about 40% of the LED market and has been a trend in LED packaging technology development in recent years.
2. Wafer-Level Packaging (WLP) LED Packaging
WLP LED packaging refers to the direct packaging and testing of LEDs on wafers, which are then diced into individual components. This packaging method eliminates the need for flip-chip and adhesive, saving on process and cost. Additionally, WLP LED packaging has smaller dimensions (CSP) and is well-suited for fine-pitch layouts.
WLP LED packaging is a relatively mature technology at present. With the development of digital electronics and high-precision instrument technology, it is expected that WLP LED packaging technology will be further improved and popularized.
3. Chip-on-Flex (COF) LED Packaging
COF LED packaging refers to the technology of assembling multiple mid-power LED chips on a flexible printed circuit (FPC) board. COF LED packaging features high thermal conductivity, high light efficiency, high flexibility, and uniform light output.
COF LED packaging is widely used in various products that require linear light sources, surface light sources, and three-dimensional light sources. It can also be used as a general-purpose LED packaging.
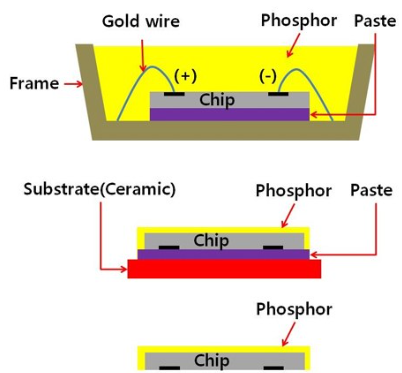
The characteristics of COF LED packaging make it suitable for various harsh environments. For example, in smartphones, COF LED packaging technology allows manufacturers to curl the leads at the bottom of the smartphone instead of placing the chips on the glass back panel. This design allows for a larger screen-to-body ratio and narrower bottom bezels in modern smartphones.
4. Modular LED Packaging
Modular LED packaging is an innovation in LED lighting technology that simplifies design and installation, improves reliability and maintainability, and provides flexibility and scalability, contributing to energy efficiency and environmental protection.
5. Inverted Packaging Form
Inverted LED chips are installed in an inverted manner on the packaging substrate. This packaging form allows light to directly emit from the bottom of the chip instead of the top. Through this design, inverted LED chips can provide higher light output efficiency and better optical performance. Inverted packaging also offers better thermal management, efficiently conducting and dissipating the heat generated by the chip. This packaging form also has a smaller package size, making it convenient for installation and integration. In conclusion, the inverted packaging form of inverted LED chips brings significant improvements and advantages to LED lighting technology.

I hope this article will give you a deeper understanding of led package. I am your editor from TCWIN, guiding you on the road to lighting.
![]() pkgled
LEDSMDBEADS
release time:2023-12-07 09:47:00
Reading volume:1
pkgled
LEDSMDBEADS
release time:2023-12-07 09:47:00
Reading volume:1




